Passing Arrays
The discussion of passing reference values in the previous section is equally valid for arrays, as arrays are objects in Java. Method invocation conversions for array types are discussed along with those for other reference types in §5.10, p. 265.
In Example 3.12, the idea is to repeatedly swap neighboring elements in an integer array until the largest element in the array percolates to the last position in the array.
Example 3.12 Passing Arrays
public class Percolate {
public static void main (String[] args) {
int[] dataSeq = {8,4,6,2,1}; // Create and initialize an array.
// Write array before percolation:
printIntArray(dataSeq);
// Percolate:
for (int index = 1; index < dataSeq.length; ++index)
if (dataSeq[index-1] > dataSeq[index])
swap(dataSeq, index-1, index); // (1)
// Write array after percolation:
printIntArray(dataSeq);
}
public static void swap(int[] intArray, int i, int j) { // (2)
int tmp = intArray[i]; intArray[i] = intArray[j]; intArray[j] = tmp;
}
public static void swap(int v1, int v2) { // (3) Logical error!
int tmp = v1; v1 = v2; v2 = tmp;
}
public static void printIntArray(int[] array) { // (4)
for (int value : array)
System.out.print(” ” + value);
System.out.println();
}
}
Output from the program:
8 4 6 2 1
4 6 2 1 8
Note that in the declaration of the method swap() at (2), the formal parameter intArray is of the array type int[]. The other two parameters are of type int. They denote the values in the array that should be swapped. The signature of the method is
swap(int[], int, int)
This swap() method is called in the main() method at (1), where one of the actual parameters is the array variable dataSeq. The reference value of the array variable dataSeq is assigned to the array variable intArray at method invocation. After return from the call to the swap() method, the array variable dataSeq will reflect the changes made to the array via the corresponding formal parameter. This situation is depicted in Figure 3.4 at the first call and return from the swap() method, indicating how the values of the elements at indices 0 and 1 in the array have been swapped.
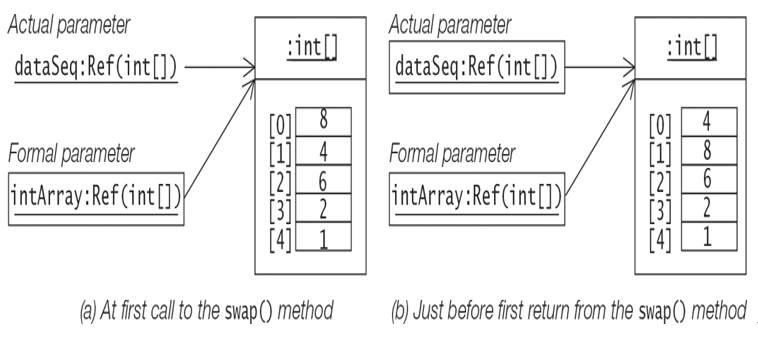
Figure 3.4 Parameter Passing: Arrays
However, the declaration of the swap() method at (3) will not swap two values. The method call
swap(dataSeq[index-1], dataSeq[index]); // Call signature: swap(int, int)
will result in the swap() method at (3) to be invoked. Its execution will have no effect on the array elements, as the swapping is done on the values of the formal parameters.
The method printIntArray() at (4) also has a formal parameter of array type int[]. Note that the formal parameter is specified as an array reference using the [] notation, but this notation is not used when an array is passed as an actual parameter.
